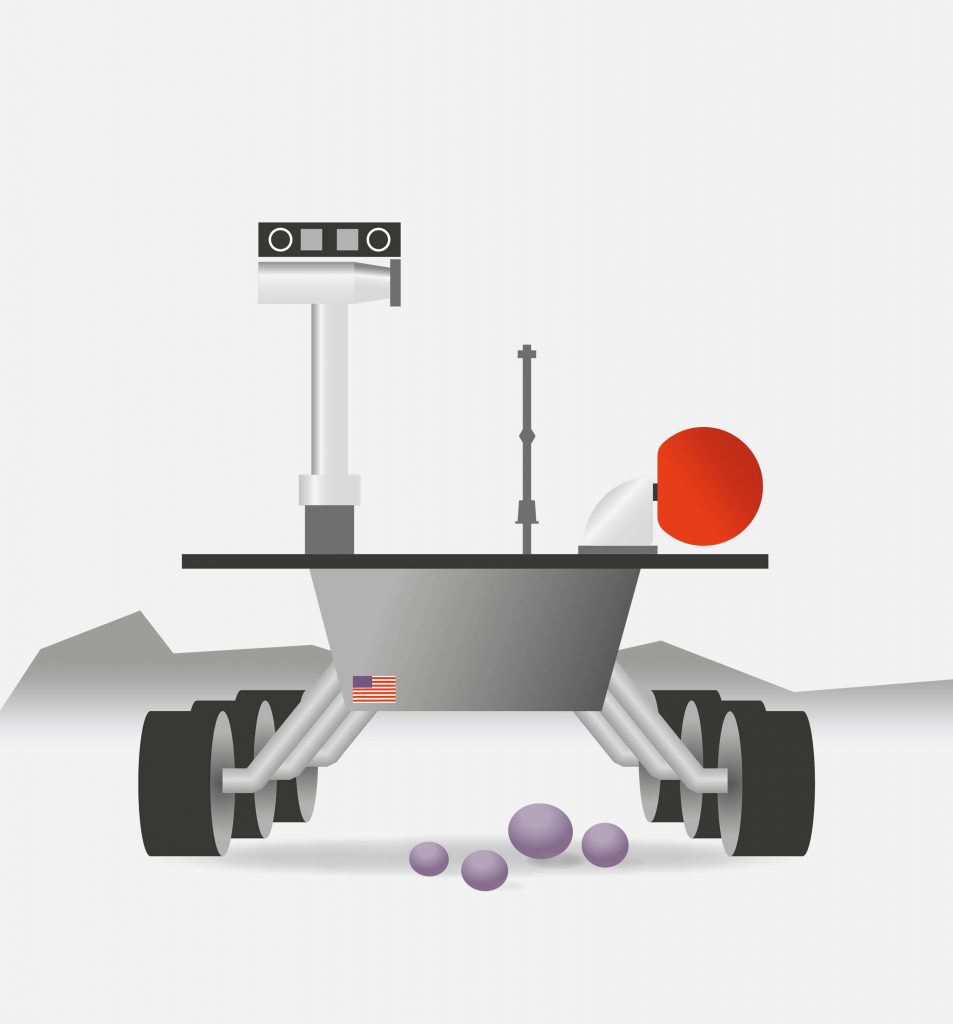
Opportunity (NASA)
Text adapted from «NASA Science Mars Exploration Program«
In January 2004, two robotic geologists named Spirit and Opportunity landed on opposite sides of the red planet. These robotic explorers have trekked for miles across the Martian surface, conducting field geology and making atmospheric observations. Carrying identical, sophisticated sets of science instruments, both rovers have found evidence of ancient Martian environments where intermittently wet and habitable conditions existed.
Since leaving their landing sites, the twin rovers have sent hundreds of thousands of spectacular, high-resolution, full-color images of Martian terrain as well as detailed microscopic images of rocks and soil surfaces to Earth. Four different spectrometers have amassed unparalleled information about the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Martian rocks and soil. Special rock abrasion tools, never before sent to another planet, have enabled scientists to peer beneath the dusty and weathered surfaces of rocks to examine their interiors.
With data from the rovers, mission scientists have reconstructed an ancient past when Mars was awash in water. Spirit and Opportunity each found evidence for past wet conditions that possibly could have supported microbial life.
Spirit found a variety of rocks indicating that early Mars was characterized by impacts, explosive volcanism, and subsurface water. Unusual-looking bright patches of soil turned out to be extremely salty and affected by past water. Opportunity found small spherules on the Martian surface that are examples of the mineral concretions nicknamed «blueberries.» Opportunity’s investigation of the hematite-rich concretions during the rover’s three-month prime mission in early 2004 provided evidence of a watery ancient environment.
Both rovers exceeded their planned 90-day mission lifetimes by many years. In 2015, Opportunity broke the record for extraterrestrial travel by rolling greater than the distance of a 42-kilometer marathon.
Resources:
https://mars.nasa.gov/mars-exploration/missions/mars-exploration-rovers/
http://mars.nasa.gov/mer/home/
https://mars.nasa.gov/internal_resources/825/
https://mars.nasa.gov/internal_resources/826/
https://mars.nasa.gov/internal_resources/827/
Date:
16 de septiembre de 2022