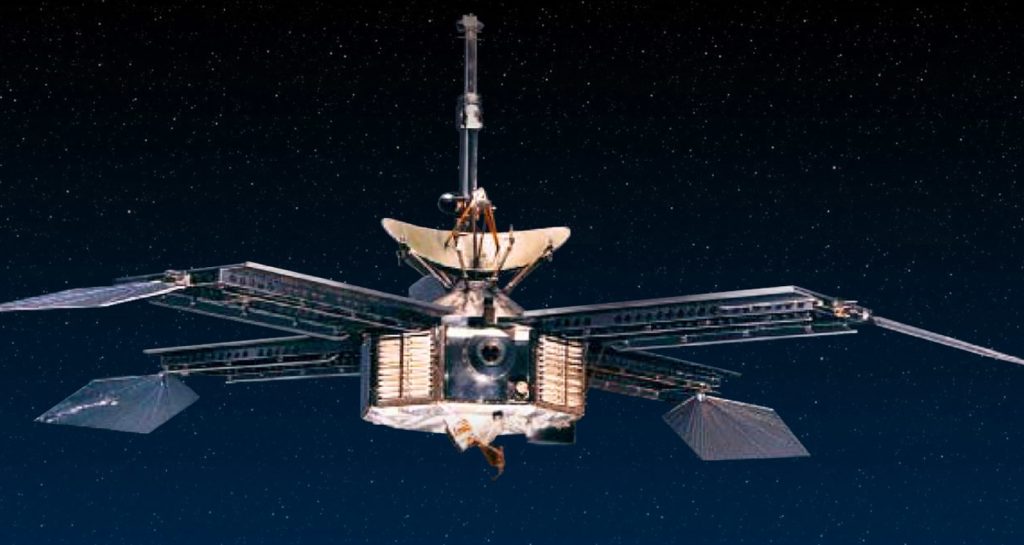
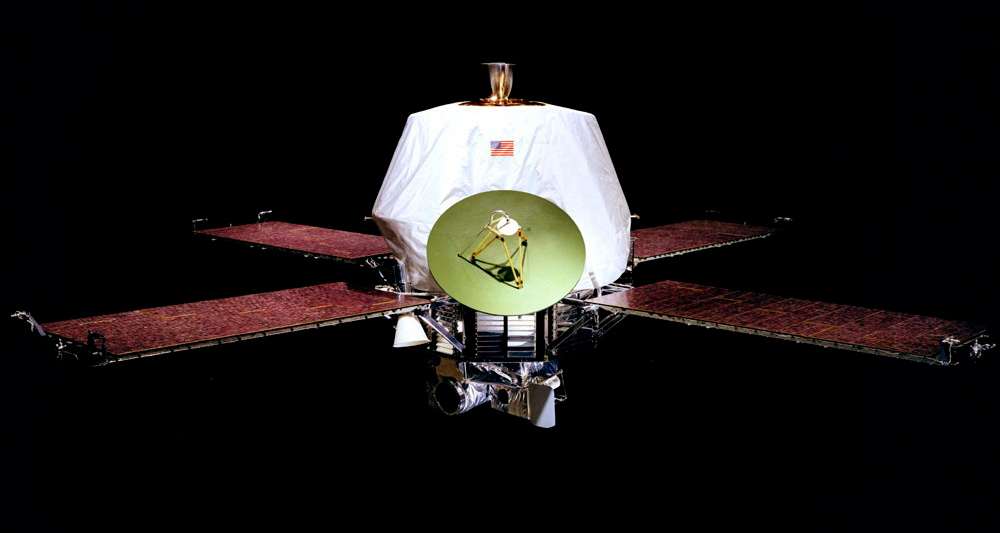
Mariner 9 (NASA)
Date:
16 de septiembre de 2022
In the early 1960s, Americans and Russians are competing to explore the solar system, specifically Mars. The Russians are the first to launch the Mars program, but all attempts fail. In 1962, NASA launched the Mariner program: ten spacecraft to explore Venus, Mercury and Mars. Precisely, on the night of July 14-15, 1965, the Mariner 4 spacecraft made history when it completed the first flyby reconnaissance of Mars after a 228-day journey from Earth.
Keep in mind that at that time there were only images of Mars from ground-based telescopes, and no details could be seen on the surface. Mariner 4 captured an impact-cratered desert. It was a complete success, but it frustrated the expectations of many scientists about Mars as a place with habitable conditions.
Mariner 4 flew by Mars, but Mariner 9, launched on May 30, 1971, was trapped by Mars’ gravity, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit another planet.
It was a resounding success as the first global map of Mars was achieved, including the first detailed views of the volcanoes, Valle Marineris, the polar ice caps, and the Phobos and Deimos satellites. It also provided information on global dust storms, the variable gravitational field by area and evidence of erosion by the wind. In total, 54 billion bits of scientific data were sent to Earth, including 7,329 photographs that covered the entire planet.
After almost a year of operations, its scientific program ended. Mariner 9 was left in Martian orbit where it continues until it finally decays onto the red surface.


16 de septiembre de 2022